Colima on Mac M2

Colima is one of my favorite tools to work on container runtimes on macOS (and Linux).
Colima launches Lima behind the scenes and sets up VMs with a container runtime and K8S.
Install Colima: See official guide here
Before we get started, let do some checks
$ docker --version
Docker version 24.0.6, build ed223bc$ kubectl version --client=true
Client Version: v1.28.2
Kustomize Version: v5.0.4-0.20230601165947-6ce0bf390ce3$ colima --version
colima version 0.5.5Local K8S cluster
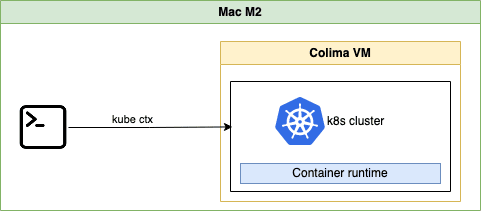
Let create Colima VM with Docker runtime, 2 CPU, 4Gi RAM, Disk 30Gi, K8S enabled.
colima start \
--runtime docker \
--cpu 2 --memory 4 --disk 30 \
--kubernetesList colima VMs
$ colima list
PROFILE STATUS ARCH CPUS MEMORY DISK RUNTIME ADDRESS
default Running aarch64 2 4GiB 30GiB docker+k3s
$ limactl ls
NAME STATUS SSH VMTYPE ARCH CPUS MEMORY DISK DIR
colima Running 127.0.0.1:64426 qemu aarch64 2 4GiB 30GiB ~/.lima/colima
$ docker context ls
NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION DOCKER ENDPOINT KUBERNETES ENDPOINT ORCHESTRATOR
colima * moby colima unix:///Users/thetran/.colima/default/docker.sockGet K8S pods
$ kubectl get po -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system local-path-provisioner-957fdf8bc-t87ps 1/1 Running 0 22m
kube-system coredns-77ccd57875-74rp6 1/1 Running 0 22m
kube-system metrics-server-54dc485875-dgmqw 1/1 Running 0 22mVerify K8S cluster setup
Let install ingress-nginx into the cluster and create simple deployment to verify our cluster setup
helm upgrade --install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx \
--repo https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx \
--namespace ingress-nginx --create-namespace
Create a simple deployment
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/quangthe/boilerplate/main/k8s/example-ingress.yaml
The output looks like this:
deployment.apps/web created
service/web created
ingress.networking.k8s.io/example-ingress createdGet deployment, service and ingress
$ kubectl get deploy,svc,ing -l=app=web
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/web 1/1 1 1 5m12s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/web LoadBalancer 10.43.53.214 192.168.5.15 8080:30314/TCP 5m12s
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress.networking.k8s.io/example-ingress nginx hello-world.info 192.168.5.15 80 5m12sSSH to Colima VM with colima ssh command and curl the ingress IP with Host header:
$ curl -H "Host: hello-world.info" 192.168.5.15/
Hello, world!
Version: 1.0.0
Hostname: web-548f6458b5-h7g2d⭐️ Bonus: Secure the ingress with cert-manager
Let's install cert-manager on the cluster and generate the self-signed certificate (use for local development) to secure the ingress.
helm install \
cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \
--namespace cert-manager \
--create-namespace \
--version v1.13.0 \
--set installCRDs=trueThen create selfsigned cluster issuer
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: selfsigned
spec:
selfSigned: {}
EOFNow secure the ingress
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
# use created selfsigned cluster issuer
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: selfsigned
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$1
labels:
app: web
name: example-ingress
namespace: default
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: hello-world.info
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: web
port:
number: 8080
path: /
pathType: Prefix
# configure tls for the ingress
tls:
- hosts:
- hello-world.info
secretName: hello-world-tls
Inside the colima vm, edit the /etc/hosts file, add line 192.168.5.15 hello-world.info, then curl the ingress by domain (-k option: ignore the self-signed certificate)
curl -k https://hello-world.info
Hello, world!
Version: 1.0.0
Hostname: web-548f6458b5-h7g2dInspect the self-signed certificate
echo | \
openssl s_client \
-showcerts \
-servername hello-world.info \
-connect \
hello-world.info:443 2>/dev/null | \
openssl x509 -inform pem -noout -textThe output will look like this
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
53:e7:85:8a:27:65:10:b3:f0:17:8c:ae:e2:61:f3:40
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Issuer:
Validity
Not Before: Sep 17 04:50:57 2023 GMT
Not After : Dec 16 04:50:57 2023 GMT
Subject:
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
Public-Key: (2048 bit)
Modulus:
00:c7:d8:dc:4e:b2:4a:ba:1d:96:50:5a:92:96:9e:
f6:cd:70:37:eb:ce:f5:e9:59:0f:da:70:1d:b4:47:
c8:51:65:79:7d:b7:21:31:f5:dc:b6:cb:40:6c:1b:
c0:28:9a:d9:3e:90:7b:92:8e:a9:75:40:07:5f:17:
c3:3d:9a:2a:e2:f2:4f:3f:be:ce:92:a9:68:6b:06:
3e:6d:5a:5b:68:d1:a8:b2:da:34:9e:49:e4:dc:bf:
85:44:ca:95:6c:23:15:c1:fe:c3:89:03:fc:47:49:
6c:87:44:eb:9c:a4:d4:c2:68:5a:ce:05:55:b9:f8:
12:27:90:e8:04:01:5f:26:ab:be:ad:50:44:89:c1:
79:9c:25:01:24:0d:d7:e5:c7:be:31:b4:35:93:84:
f3:53:f2:6a:10:69:53:55:12:dc:e7:89:d1:ea:7d:
86:ed:e0:51:47:46:ab:3b:37:94:49:28:58:22:53:
2e:52:50:d5:57:b8:5b:12:e1:ce:17:00:e4:7f:1d:
e1:b5:64:21:34:69:d9:c3:46:e0:4d:e0:35:8e:c2:
38:c4:c7:ed:a6:26:a7:c1:67:bb:f4:5c:b7:0c:67:
10:13:33:12:e0:b0:83:8c:74:24:00:98:be:8a:fe:
b6:91:cf:19:47:a3:b6:aa:7a:66:e8:2f:8b:8e:6b:
7e:a9
Exponent: 65537 (0x10001)
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Digital Signature, Key Encipherment
X509v3 Basic Constraints: critical
CA:FALSE
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name: critical
DNS:hello-world.info
Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
Signature Value:
2f:0a:63:53:af:c0:94:4f:e4:6d:fd:02:40:c0:d0:bb:e7:00:
65:3c:5c:fa:da:81:70:65:00:9d:75:c5:1d:e6:e9:91:ee:25:
9f:50:22:dd:d7:f3:57:12:79:39:b4:bf:08:9b:37:71:d2:68:
81:8c:df:1f:64:a3:c3:d5:be:72:97:35:b6:30:7e:6e:ee:cf:
2a:1b:59:83:b1:9a:ba:3f:52:b9:f2:68:d1:d4:b8:60:15:49:
86:11:16:0f:31:0f:29:7e:3f:8f:fe:05:c1:ed:13:41:c3:58:
c6:78:72:e4:de:7c:66:ed:0e:e7:74:c7:33:bc:57:69:a2:5b:
62:7d:0c:df:fe:8a:78:0b:64:12:c7:08:39:c1:fe:a9:0a:47:
26:37:3c:14:63:93:7c:75:81:d4:54:f8:94:9c:05:c1:3c:d2:
c5:0b:52:8e:67:31:8f:f0:ed:f0:17:7a:db:3b:6f:c0:cc:78:
62:ac:5c:fd:b2:af:42:04:77:d1:12:df:ca:e9:f3:66:a3:d6:
f0:b6:0a:c9:35:9e:bd:f9:29:66:91:9a:06:51:59:03:b5:e0:
45:74:92:3a:e9:34:cb:a5:b6:6e:f1:00:3d:cc:db:46:b9:1e:
65:b3:6a:57:c4:86:92:9e:6f:62:fa:27:d7:df:fc:89:a9:37:
b9:fc:a1:cdHappy K8S! 😎
Local Docker runtime
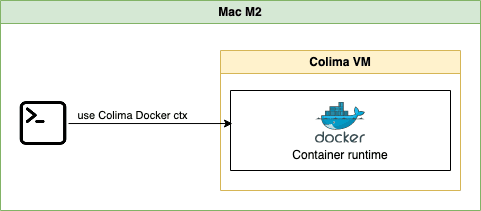
Let create Colima VM with profile named docker, Docker runtime, 2 CPU, 8Gi RAM, Disk 60Gi. We can use this docker runtime for local development with Docker.
colima start \
--profile docker \
--runtime docker \
--cpu 2 --memory 8 --disk 60$ colima ls
PROFILE STATUS ARCH CPUS MEMORY DISK RUNTIME ADDRESS
default Running aarch64 2 4GiB 30GiB docker+k3s
docker Running aarch64 2 8GiB 60GiB dockerCheck docker context
docker context ls
NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION DOCKER ENDPOINT KUBERNETES ENDPOINT ORCHESTRATOR
colima moby colima unix:///Users/thetran/.colima/default/docker.sock
colima-docker * moby colima [profile=docker] unix:///Users/thetran/.colima/docker/docker.sockTips: Switch docker context with docker context use <ctx-name>
Let build a sample Dockerfile
FROM alpine:3
RUN apk add curlDockerfile
docker build -t alpine:curl .Check the image build
$ docker image ls
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
alpine curl c961778c5283 5 seconds ago 14MBSSH to Colima VM, we can get docker images as well ☺️
colima ssh -p docker
colima-docker:/Users/thetran$ docker image ls
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
alpine curl c961778c5283 2 minutes ago 14MBClean up
$ colima ls
PROFILE STATUS ARCH CPUS MEMORY DISK RUNTIME ADDRESS
default Running aarch64 2 4GiB 30GiB docker+k3s
docker Running aarch64 2 8GiB 60GiB dockerDelete Colima VM with colima delete -p <profile-name>
colima delete -p docker
# without -p, it will delete profile `default`
colima deleteHappy container! 😎